According to the IUSN Red List, more than 28,000 species are at risk of extinction. This is 27% of all species evaluated so far. Here is a list of several species that still survive in captivity but do not live or grow in the wild.
Encephalartos Woodii
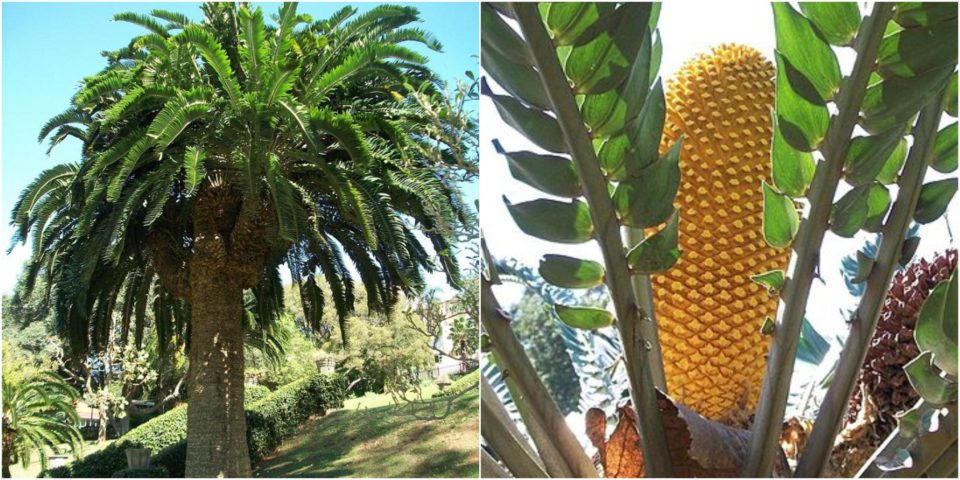

It is one of the world’s rarest plants that has already died out in the wild. For this reason, it is one of the most expensive, if at all possible to obtain. Several centimeters offsets cost tens of thousands of dollars.
In 1907, only one male tree was found in the wild and was moved to London’s Kew Botanical Garden. The tree comes from South Africa‘s Ngoya Forest, and all the current plants in the world’s collections come from its offshoots. They are also only males. So the seeds of this plant do not exist.
Franklin Tree (Franklinia alatamaha)
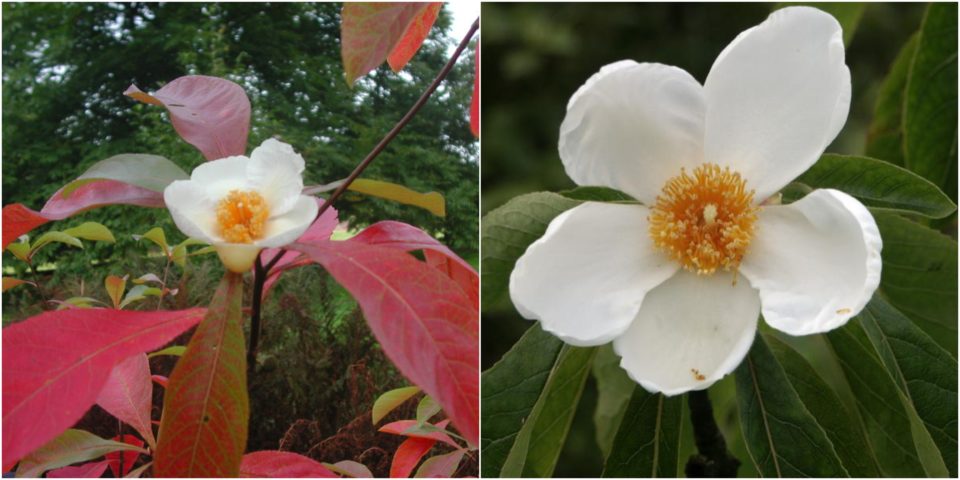

It comes from the Altamaha River Valley in Georgia in the southeast of the United States. It has been extinct in the wild since the early 19th century, but survives as a cultivated ornamental tree.
Cyanea Superba
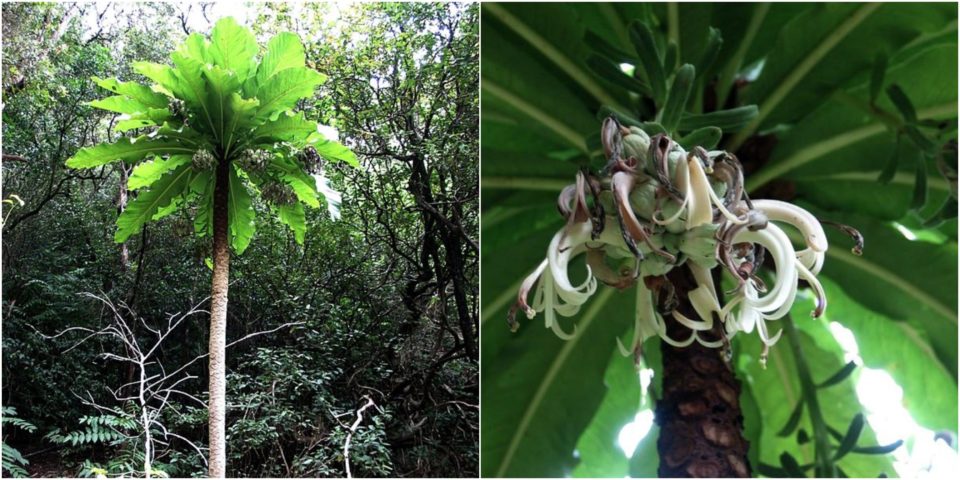

is a rare species of flowering plant, commonly known as Mt. Kaala cyanea or superb cyanea. It is endemic to the Hawaiian island of Oahu. It exists in cultivation and some individuals have been planted in appropriate habitat. It is a federally listed endangered species of the United States.
Kokia Cookei
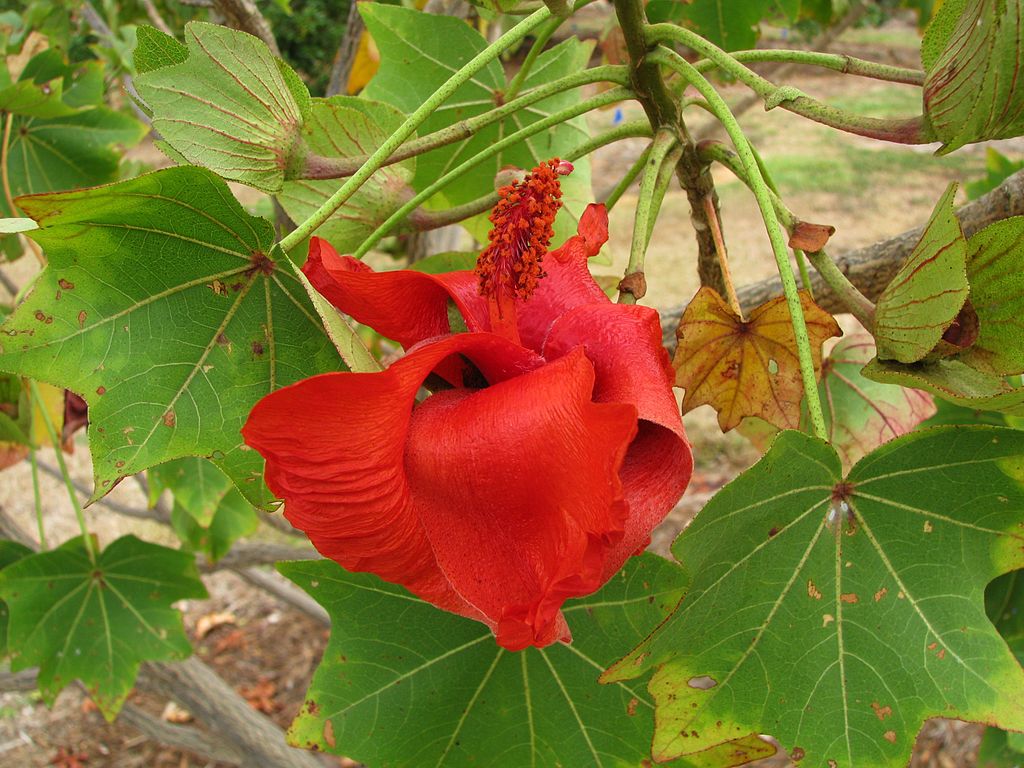

his species is only known to have existed in the lowlands of western Molokaʻi island of the Hawaiian Islands.It is considered one of the rarest and most endangered plant species in the world. A single plant was discovered on the same Kauluwai. Although this tree was destroyed in a fire in 1978, a branch that was removed earlier was grafted onto the related, and also endangered, Kokia kauaiensis. Currently there exist about 23 grafted plants
Currently, the IUSN Red List contains 35 species of plants that you cannot find in the wild, yet there is a chance to see them in botanical gardens.
Source and credit: Wikipedia.org, wikimedia.org, iucnredlist.org, John S. Donaldson, flickr.com