By 2050, the world’s population is expected to be close to 10 billion. Scientists say that due to industrial development and urbanization the Earth has lost a third of its arable land over the past 4 decades. We do not know how much more we will lose in the next 40 years. Increasing food demand as a result of the growing population is one of the biggest challenges we face.
Modern agriculture brings various topics. One of them is vertical farms, which are one of the fastest growing segments of agriculture. In 2010 there was only one vertical farm in Japan, three in 2013, in Japan, the USA, and South Korea. Today, there are tens to hundreds of vertical farms, including fully automated farms, with a wide use of artificial intelligence.
What a Vertical Farm Is
This method produces food in vertically stacked layers that are commonly integrated into other structures such as a skyscraper or shipping container. Using Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA), this modern idea uses indoor farming techniques.
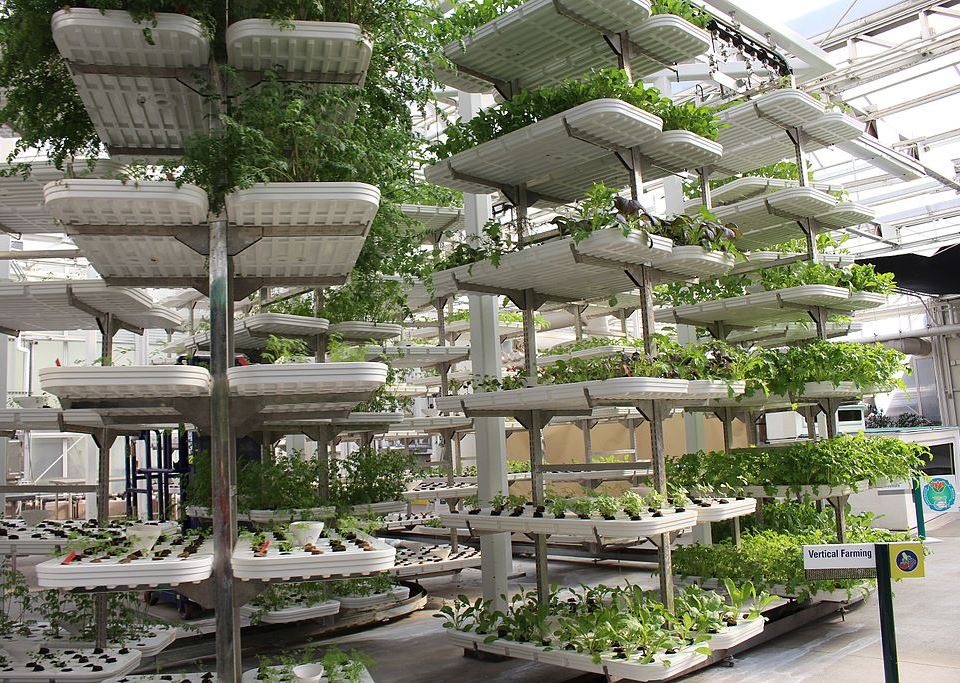

The essence of a vertical farm is based on the in vitro model of plant cultivation, i.e. in fully controlled indoor conditions. These procedures are a common part of breeding practice.
It is a modern way of agriculture using modern technologies. Crops are grown in layers on top of each other on vertically inclined flats in a small area; so it’s possible to grow more crops can be grown than on a conventional outdoor farm.
Every Day Harvest
The advantage of such a plant is that it does not take into account the season and produces crops 365 days a year. Vegetables draw nutrients from a special solution and factors such as temperature or humidity are strictly controlled to create ideal conditions and maximize yield. Farms often use a combination of natural sunlight along with specially developed LED lights.
Advantages
Water saving is fascinating. Water consumption is an incredible 90 – 99 percent less compared to water demand on an outdoor farm. Vertical farms practically do not use pesticides, growth regulators and excipients. Another advantage is the saving of cultivated area, i.e. agricultural or natural land.
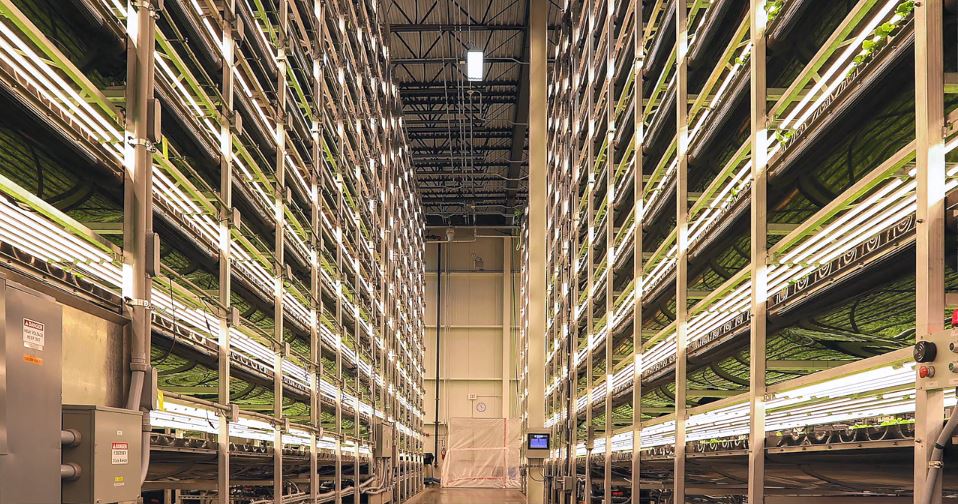

Countries that have to import most of the food, such as the United Arab Emirates (imports 85%), can greatly reduce their footprint if they significantly reduce their food transport to the country.
Disadvantages
On the other hand, it must be acknowledged that farms have higher energy requirements and are far from suited to growing everything.
Dutch professor Leo Marcelis from the University of Wageningen says there is still a need for a number of researches into reducing energy consumption by vertical farms. “Currently, manufacturers are working on LED technology that will improve the process of converting electricity into light. At the same time, we are also looking for ways to grow plants using less light, or to produce more plants with the same amount of light,”says Marcelis.
There are no pollinators on farms. It is therefore necessary to pollinate the plants manually, which increases labor costs.
Visions of the 21st Century
The Market Watch study estimates that the global market for vertical farms should grow by 24.8% annually to a total of $ 5.8 billion by 2022. The focus of their expansion is Asia and North America.
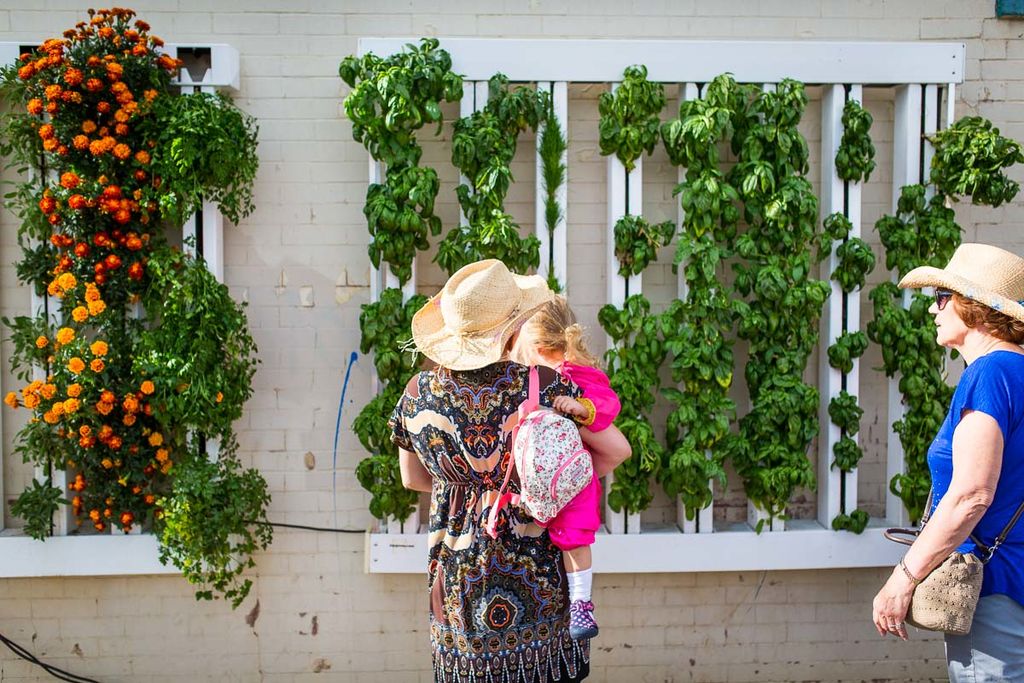

In practice, there are globally different natural and economic assumptions in different geographical areas. Especially in the countries of East and South Asia, which suffer from overpopulation and a shortage of arable land, there are significant assumptions; and in countries with extremely poor natural conditions for agricultural development, such as Saudi Arabia and other Gulf countries and their neighboring countries.
The development of vertical farms can be expected in generally innovative countries with sufficient capital, such as the USA.
Vetical farming can help to feed growing world popullation.
Source & credit: commons.wikimedia.org,flickr.com,vimeo.com/280567373,https://vimeo.com/259346181