A four-legged robot now guards the state of the archeological park in Pompeii. According to the park management, it is suitable for mapping smaller or less accessible places. The conservationists also want to use the robot to monitor possible illegal archeological excavations.
Excavations in Pompeii Continue
The ancient city of Pompeii, located near Naples, was destroyed during the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD. The Roman cities of Herculaneum, Stabiae, and Oplontis were also covered with ashes or flooded with lava and mud. Today, there are large archeological parks in some of these cities, where scientific research is still ongoing.
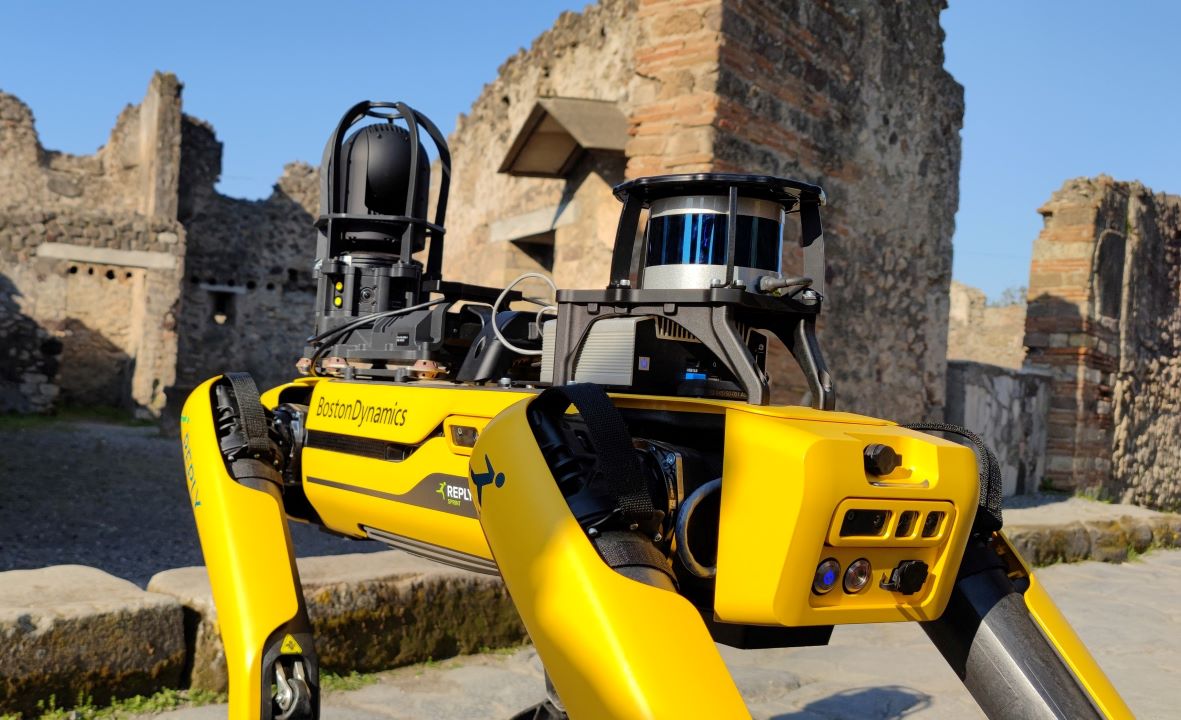

The administration of the archeological site in Pompeii began to use a modified SPOT robot from the American company Boston Dynamics. The device resembles a smaller dog and can move quickly on various surfaces.
The Robotic Dog Monitors Hard-to-reach Places
The robot can be programmed to control, and map activity is largely automatic. Thanks to the camera and 3D scanner, it will be able to automatically check the status of monuments and collect data about them.
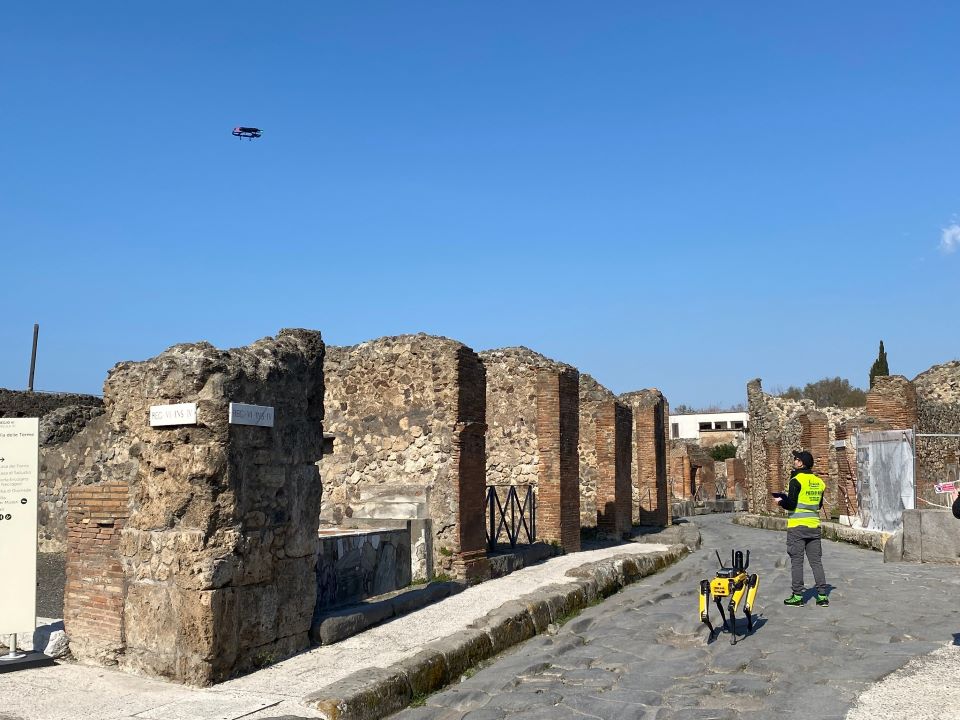

The four-legged robot is especially suitable for mapping smaller and narrow places where it is otherwise difficult to get. “We also want to test the use of these robots in tunnels dug by unauthorized searchers,” said Gabriel Zuchtriegel, head of the archeological park. The security conditions in these tunnels are usually very poor, so robots could help map this illegal activity.
In addition to the robot, a classic flying drone is also tested in Pompeii, which can easily monitor the entire large area from a height and thus monitor places where the robotic dog cannot see.
Source and credit: https://www.facebook.com/pompeiisoprintendenza/