Man is afraid that he will come into contact with some types of bacteria, on the contrary, he appreciates others for their beneficial work in our intestines. Researchers in Hong Kong have found that one type of dreaded bacterium can be useful in our environment – in purifying water from microplastics.
80% of the Dreaded Bacteria Are in Biofilms
Bacteria and other microorganisms form biofilms – slimy material of a polysaccharide nature on various types of surfaces, where they clump together and protect themselves from environmental influences.
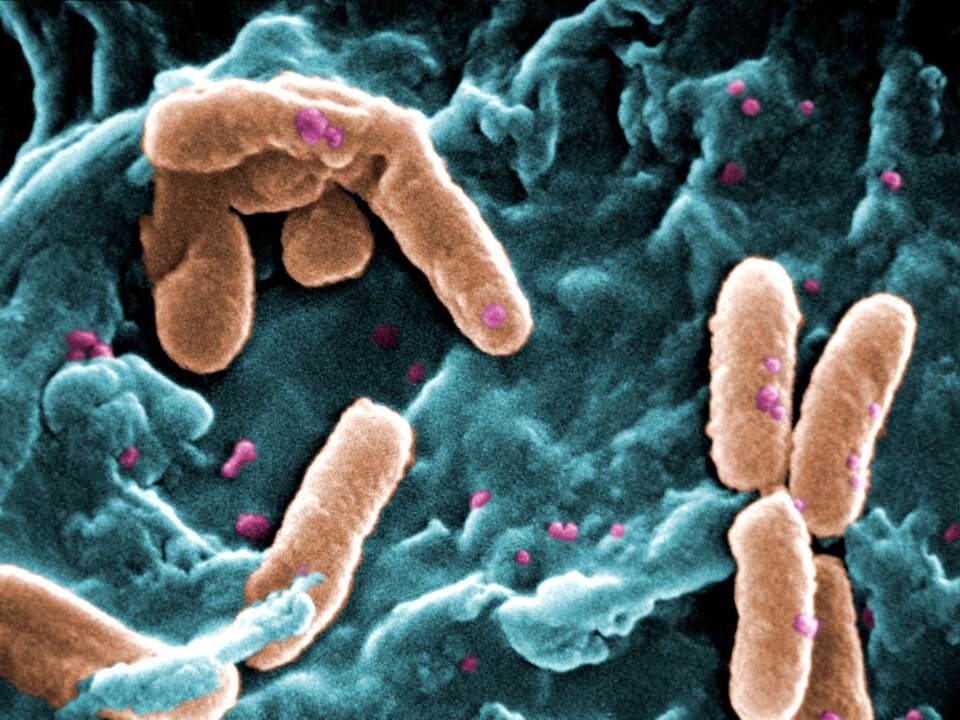
In the case of a bacterial infection, bacterial biofilms often cause troubles because they usually increase the resistance of the bacteria, which can complicate treatment. According to some estimates, up to 80 percent of these infections involve bacteria in biofilms.
Cleaning Water Using Bacterial Biofilms
Bacterial biofilms can be very beneficial. For example, they have been used for a long time in wastewater treatment. The research team of Hong Kong Polytechnic University relied on this fact when it used an adhesive bacterial biofilm to capture plastic microparticles in water.

The researchers used biofilm as a biological network. They chose a biofilm of Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteria that endanger humans – they cause otitis media, urinary tract infections, gingivitis, or endocarditis.
The Undemanding Bacterium Succeeded
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is not environmentally demanding and has previously been shown to have no problem with the colonization of microplastic particles. The researchers conducted a series of experiments in a bioreactor, where they exposed the biofilm to passing microplastics.

The researchers found that the biofilm encapsulates a group of microplastics, which then sinks to the bottom of the vessel. It is possible to add a specific gene to the biofilm, which causes rapid disintegration of the microplastics. This step releases the microparticles from the biofilm, so they can be removed and recycled.
Source: https://www.eurekalert.org/pub_releases/2021-04/ms-umt042621.php, feeatured image by Arek Socha from Pixabay