A ten-minute eye-to-eye interaction can cause hallucination-like states. An Italian psychologist tested 50 volunteers. The results were more than interesting: the volunteers saw animal faces, strange creatures, and the faces of the dead. Mirror neurons probably played a key role.
Volunteers Saw the dead and Other Strange Creatures in the Mirror
Italian psychologist Giovanni Caputo of the University of Urbino locked fifty volunteers in a room equipped with mirrors and gave them a seemingly simple task: observe their own image for ten minutes.
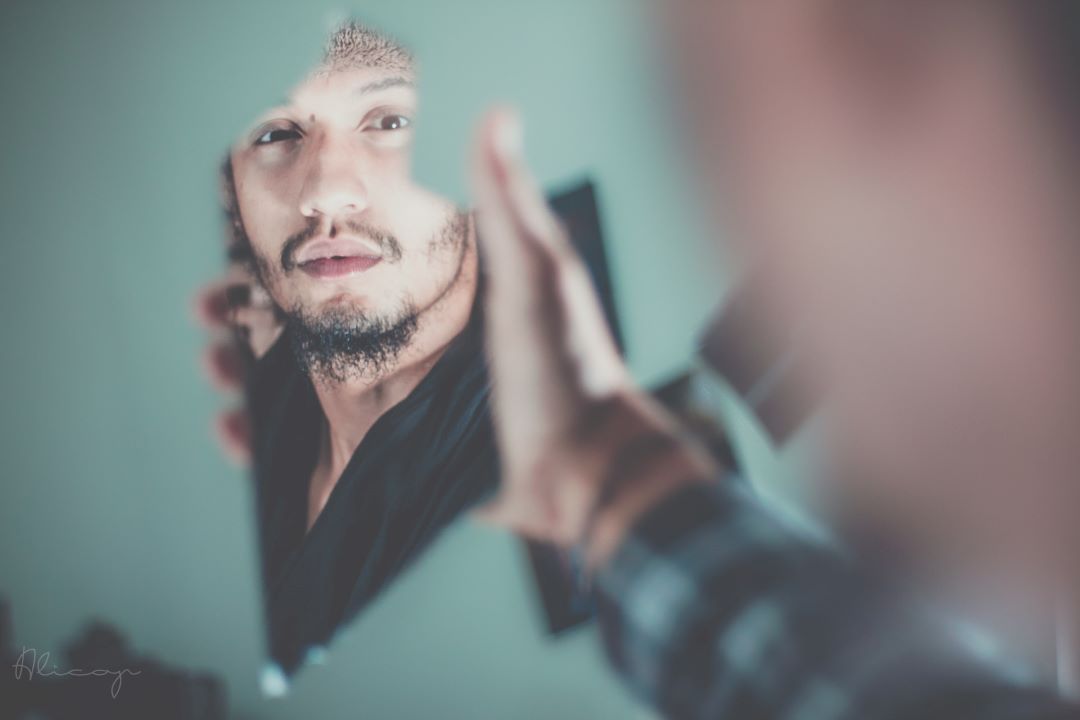

At one point, the participants said, their faces began to take on unusual features that resembled an animal’s face. Instead of their own faces, many saw the faces of deceased ancestors, various supernatural creatures, and monsters.
Eye-to-eye Gaze Experiment Induced Hallucination-like States
Caputo repeated the experiment, except that the eyes of another living person replaced the original mirrors. And as it turned out, the participants had even more remarkable experiences this time. Forty volunteers were divided into two groups, each group in pairs.

While members of the first group were asked to sit back-to-back and stare at a bare wall, the second group was asked to sit opposite each other at one meter – face to face. Within ten minutes, the pairs staring at each other’s eyes had the same conditions as the volunteers in the first experiment.
The illusory imagery was replaced by experiences reminiscent of events in a dream. Looking into the other person’s eyes induced an altered perception of colors, which suddenly appeared more intense and brighter than usual. They could hear unnaturally loud sounds, many even felt as if they were outside their own bodies, and time suddenly seemed to pass more slowly than usual.
Did Brain Synchronization Lead to Empathy?
During the experiment, Caputo noted another interesting finding: the associative experiences of the pair of people observing each other usually occurred at the same time, as if their brains could synchronize with each other.

Neuroscientists offer the theory that this is the ability to empathize with another based on their expression. Thanks to so-called mirror neurons, the human brain has the ability to imagine another person’s feelings or experiences, to see facial expressions. Thus, one can easily understand that the other person feels pain and feels it himself for a short time. Mirror neurons may have played a key role in the experiment with the hallucinogenic eye-to-eye gaze.
These are all manifestations of the so-called dissociation, i.e., an altered state of consciousness – which can otherwise be induced in only a few ways, namely by hallucinogenic substances, hypnosis, or sensory deprivation.
Source and credit: https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/0276236620969632, featured photo by Colin Lloyd on Unsplash